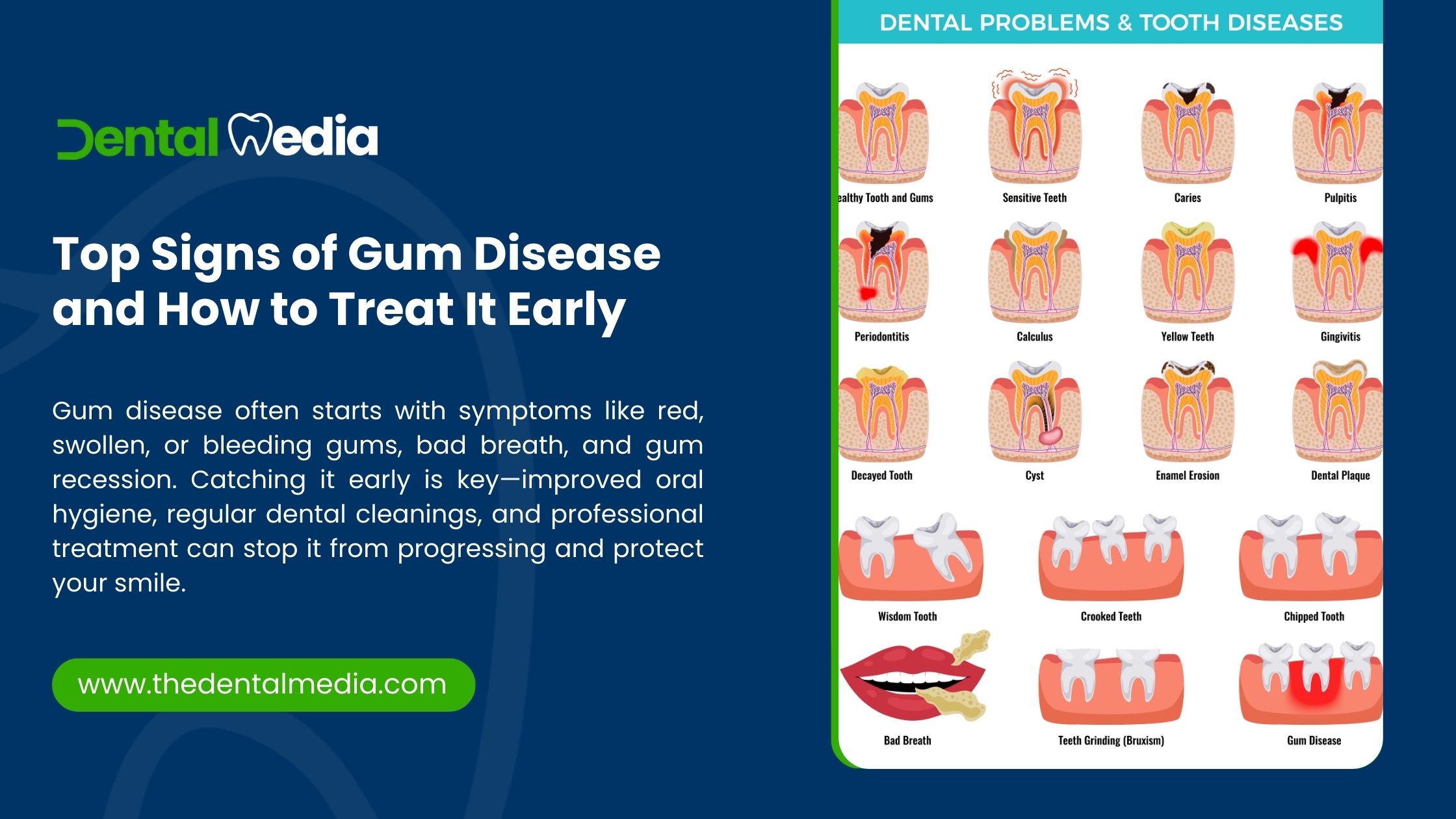
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common but often overlooked dental condition that affects the tissues supporting your teeth. Left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and has been linked to systemic health issues like heart disease and diabetes. The good news? Gum disease is preventable and treatable—especially when caught early.
What Is Gum Disease
Gum disease is an infection of the gums caused primarily by plaque buildup—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. There are two main stages:
- Gingivitis: The earliest and mildest form of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums.
- Periodontitis: A more advanced stage where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected. This stage can lead to bone loss and tooth loss if not treated.
Top Signs of Gum Disease
Recognizing the early signs of gum disease is crucial for prompt treatment. Here are the most common symptoms:
1. Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums
Healthy gums should be firm and pink. Inflammation is often the first visible sign of gingivitis.
2. Bleeding Gums
If your gums bleed when brushing or flossing, it’s a warning sign. While many people think this is normal, it usually indicates underlying gum irritation.
3. Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Chronic bad breath that doesn’t go away with brushing may be caused by bacteria buildup under the gum line.
4. Receding Gums
If your teeth look longer than they used to, your gums may be pulling away from the teeth—a sign of periodontitis.
5. Loose or Shifting Teeth
As the disease progresses, it can affect the bone supporting your teeth, leading to mobility or changes in bite alignment.
6. Pain When Chewing
Discomfort or sensitivity while chewing may indicate underlying infection or bone loss.
7. Pus Between Gums and Teeth
This is a clear sign of infection and requires immediate professional care.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of gum disease is poor oral hygiene, but several factors can increase your risk, including:
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, menopause)
- Diabetes
- Genetics
- Medications that reduce saliva flow
- Poor nutrition
- Chronic illnesses
How to Treat Gum Disease Early
1. Improved Oral Hygiene
Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing once a day, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help remove plaque and prevent gingivitis from progressing.
2. Professional Dental Cleaning
Routine dental cleanings remove tartar (hardened plaque) that cannot be removed at home. If caught early, gingivitis can often be reversed with professional cleanings and good home care.
3. Scaling and Root Planing
For more advanced gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be needed. This involves cleaning below the gumline to remove plaque and smooth the root surfaces, helping gums reattach to the teeth.
4. Medications
In some cases, your dentist may prescribe topical antibiotics, antimicrobial mouth rinses, or oral medications to control infection and inflammation.
5. Surgery (Advanced Cases)
If the disease has progressed significantly, surgical options like flap surgery or bone grafting may be required to restore damaged gum and bone tissues.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
- Brush and floss daily
- Visit your dentist regularly (every 6 months or as recommended)
- Avoid smoking and tobacco
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Manage health conditions like diabetes
When to See a Dentist
You should see a dentist if you experience any symptoms of gum disease, especially if they persist for more than a week. Early intervention is key to preventing long-term damage.
For more help and support, feel free to contact us at TheDentalMedia.com.